CH2. 프로토콜 아키텍처와 TCP/IP, 인터넷기반 애플리케이션
2024년 3월 19일 작성
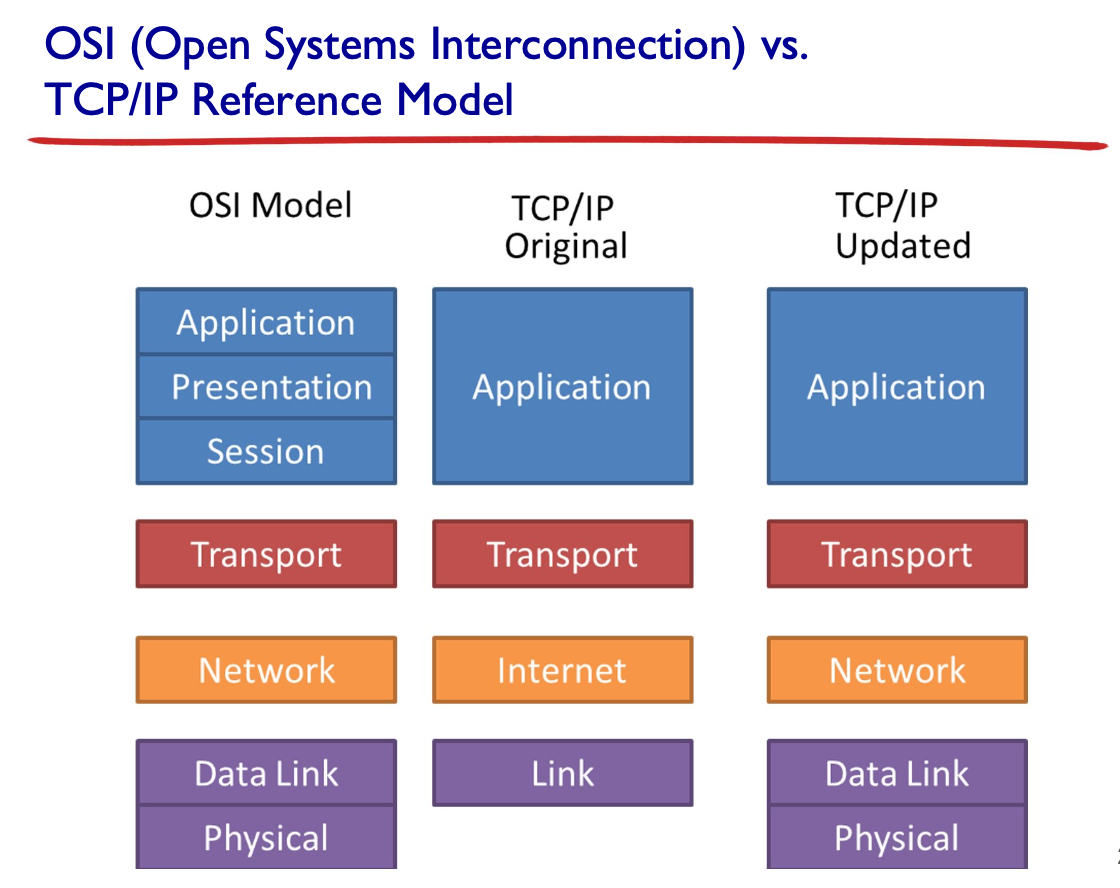
Define a protocol
Using a layered protocol stack, communication function is broken down into sub-functions implemented at each layer. A protocol at a layer N in a device communicate with the same protocol at the same layer N in another device by exchanging messages (control info. in header + payload). % payload 란 각 프로토콜이 최종 전송하고자하는 데이터로 상위계층으로 부터 받는 message 임.
서로 다른 두 장비에서 같은 계층의 동일한 모듈이 서로 주고 받을 데이터들의 format (syntax), 각 데이터 내용의 의미 (semantics) 그리고 주고 받는 데이터들의 순서와 행동을 정의한 것, 즉 해당 모듈이 수행할 작업을 완성하기 위해 두 모듈사이에 지켜야할 규칙의 집합이 프로토콜 임.
Internet communication system is based on the peer layer protocol architecture. Each layer protocol (ex. TCP) is a service user to its adjacent lower layer protocol (ex. IP) and a service provider to its adjacent higher layer protocol (ex. HTTP). 즉, 데이터통신의 5계층 모델에서 각 계층(N계층)의 프로토콜들이 수행하는 작업은 자신 보다 바로 아래(N-1) 계층(lower layer)의 프로토콜이 제공하는 서비스를 사용하여 이뤄지므로 아래 계층 프로토콜이 제공하는 서비스의 사용자에 해당한다. 또한, 결과적으로 자신의 바로 상위(N+1) 계층(higher layer)의 프로토콜에게 필요한 서비스를 제공하게 되므로 상위 계층 프로토콜에게는 service provider의 역할을 하게 된다.
- SAP(Service Access Protocol): 인접한 두 layer 프로토콜 사이의 인터페이스를 말함 ; 특별히 application layer와 transport layer 사이의 TSAP을 socket (소켓)이라고 함 ; 앱 개발자는 socket programming 만으로도 네트워크에 관한 지식없이 네트워크 프로그래밍이 가능함.
Role of each layer in the Internet (TCP/IP) protocol stack L5) Application L : Support network Application service btw src & dst hosts ; HTTP (web serfing), SMTP(email), etc.; 각 프로세스는 상이한 port number를 이용함. L4) Transport L : (상위 5계층 프로세스의 port # 를 이용하여) process-to-process comm. btw src & dst hosts; TCP, UDP, etc L3) Network L : (상위 4계층 프로토콜이 있는 호스트의 IP주소를 이용하여) host-to-host comm (routing to destination host); IP L2) Data Link L : (L1 계층에 따라 상이한 주소와 알고리즘을 이용하여) data transfer between physically adjacent nodes; Ethernet, Wi-Fi, HDLC, etc
Application (L5) and transport(L4) layers exist only at end nodes (hosts or stations) and does not in network nodes (routers).
L2 - Data Link layer
L3 - Network layer (host-to-host)
- delivery 서비스를 제공하는 계층이다.
- packet by packet 으로 destination으로 라우팅해준다.
- 라우팅 기능을 제공 - Internet Protocol 을 활용한다.
- end systems: source는 default router에게 보내고, receiver도 그의 default router에게 받는다.
L4 - Transport Layer
Process-to-process 프로토콜
애플리케이션에서는 sender와 receiver가 같은 컴퓨터에 있는 것처럼 논리적으로 구현함 TCP 헤더에는 Port 넘버가 들어가게 된다
L5 - Application Layer
- 각 애플리케이션마다 분리된 모듈이 필요
Traditional vs. Multimedia Application
- 전통적인 L5: Loss-sensitivity - TCP를 call 한다. reliable 한 서비스를 필요로하는 application
- SMTP
- FTP
- SSH TCP는 안정적인 서비스를 제공하기 위해 부가적인 절차가 필요하다.
- 멀티미디어: 이런 프로토콜들이 생겨남. IP 계층에서 QoS를 높이기 위해. -> delay variability
- RTP
- SIP
Addressing level
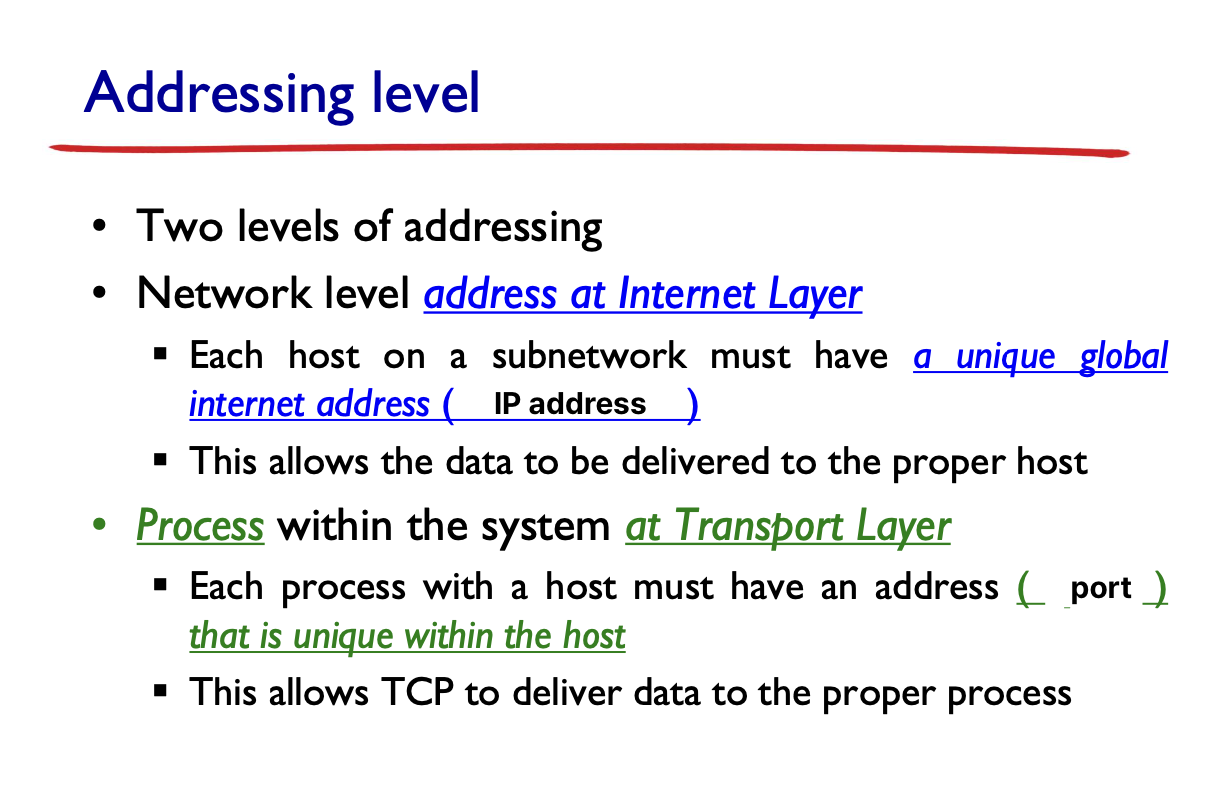
port는 host 안에서만 유니크하면 된다.
Addressing
- 두 수준에서의 addressing이 필요하다.
- Port
- IP Address
Operation of TCP/IP
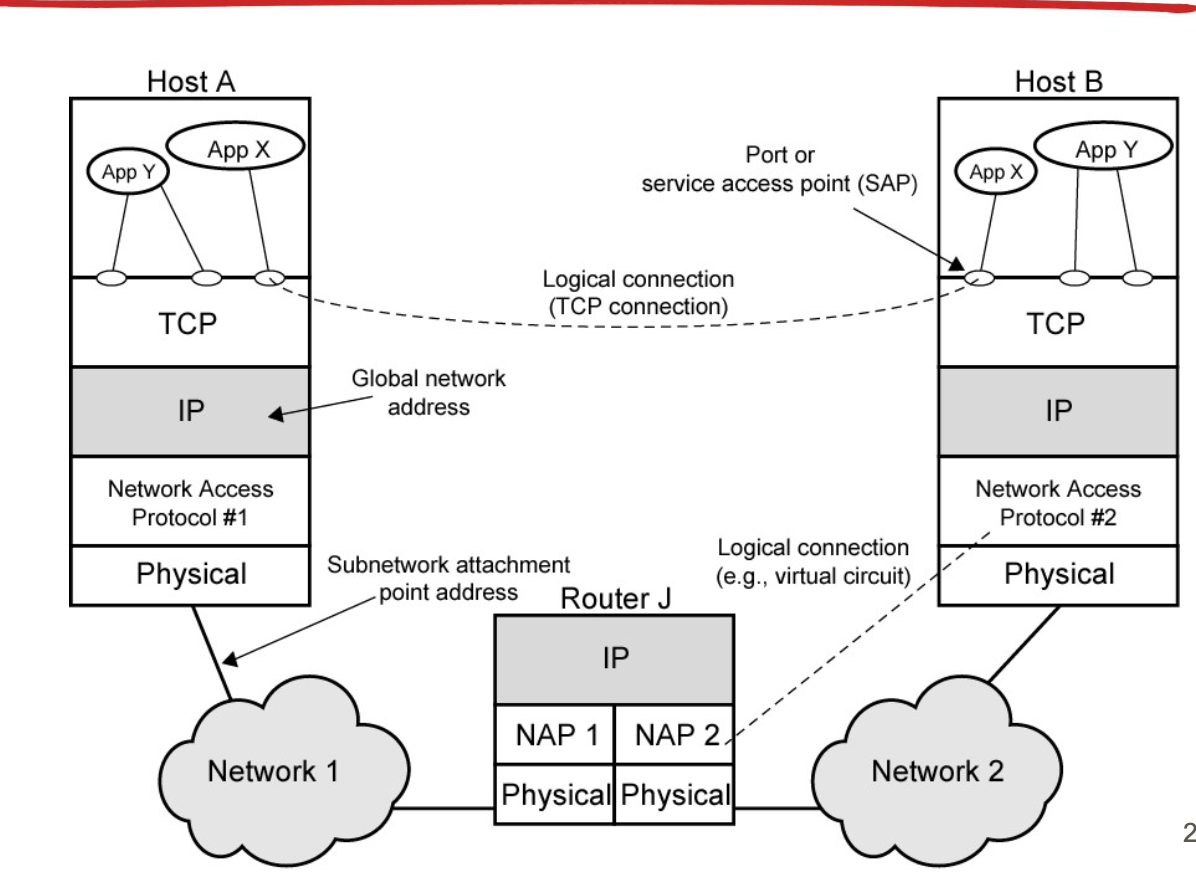 L2 address에는 종류가 여러가지 있다. 그 중 두개만 본다면
L2 address에는 종류가 여러가지 있다. 그 중 두개만 본다면
- MAC: 48-bit -> LAN 에서 널리 사용됨
- HDLC: 7-bit -> WAN에서 널리 사용됨
그러나 우리는 L3와 L4에서의 주소를 중점적으로 보고 있는 것.
Protocol Data Unit, PDU
PDU는 아래 두 가지의 combination이다.
- Payload that includes data from the next highter layer
- Header that includes control information at my layer
- used by the peer protocol at another computer.
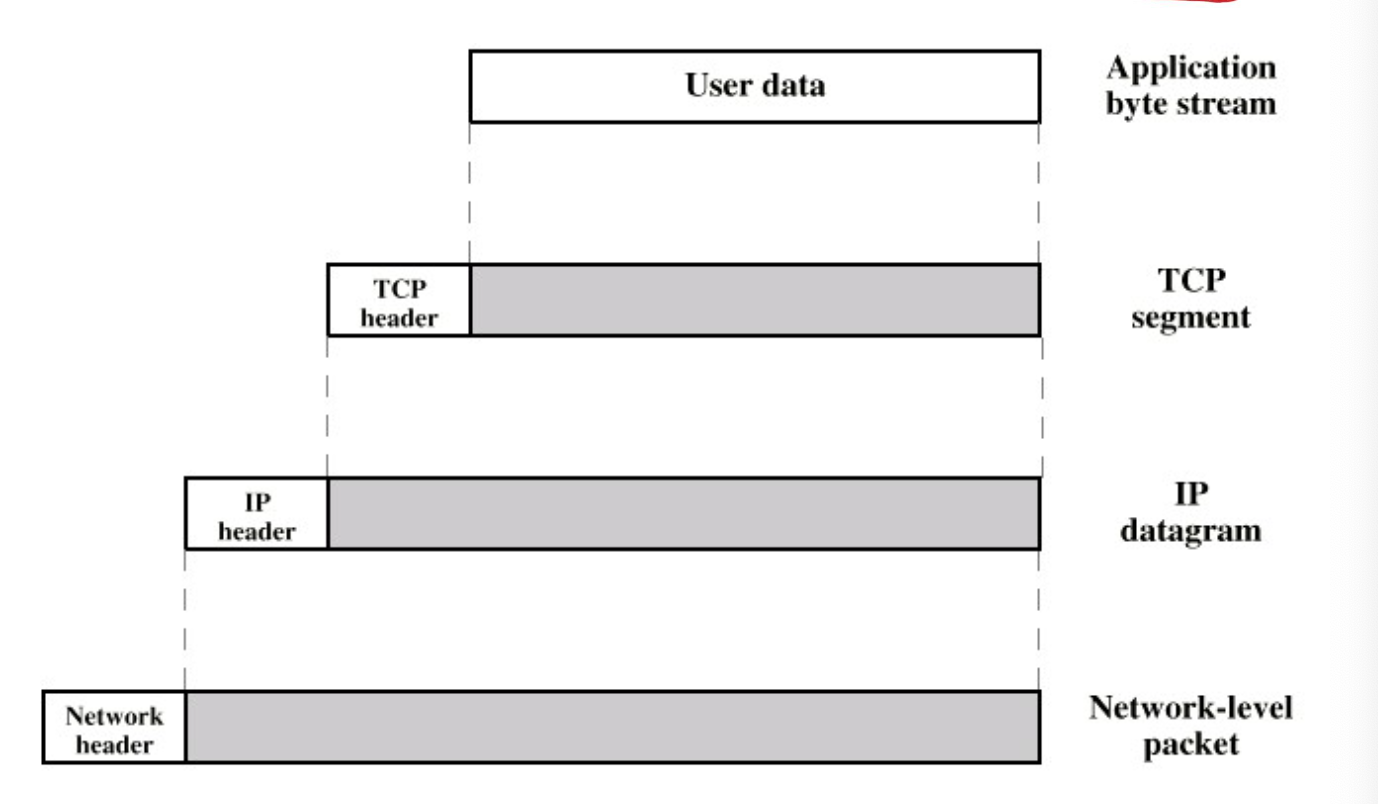
- Network-levet packet:
Frame이라고 부른다. - IP datagram:
Packet이라고도 부른다. - TCP segment
- Application byte stream: 유저 데이터,
Message라고도 부른다.
TCP at L4
- Each entity
-> in-order & no-loss delivery -> not to overflow buffer
UDP, User Datagram Protocol
-
No guarantee of delivery
-
Nopreservationofsequence
-
No protection against duplication • Minimum overhead
-
Adds port addressing to IP
-
Application using UDP
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
- DNS (Domain Name System) for query/reply
- HTTP for Real-time streaming services
-
에러 detection은 하지만, correction을 안하는 것 뿐임.
Internet Protocol & IPv4 vs. IPv6
왜 v6가 나왔을까?
-
처음 IPv4 프로토콜을 디자인했을 때, 32bit가 모자를지 몰랐음.
-
IPv6의 가장 큰 등장 이유는 IPv4 address depletion이다.
- IPv6는 v4의 네 배 크기다.
-
Physical Layer 기술의 발전으로 에러가 많이 없어져서 checksum을 없앰.
- 기존에는 라우팅에러로 쓸데없는 리소스 낭비를 줄이기 위해 checksum을 활용했었음.
-
라우터 안에서 Fragmentation 을 없앰.
정리
- source의 N 계층에 있는 프로토콜에서 만든 데이터는 destination의 N계층에서만 읽고 수행하게 됨.
- 5계층, 4계층 사이의 SAP를 socket이라고 한다.
Service Primitives and Parameters
Function call의 관점에서 보면 primitives와 parameters를 구분할 수 있다.
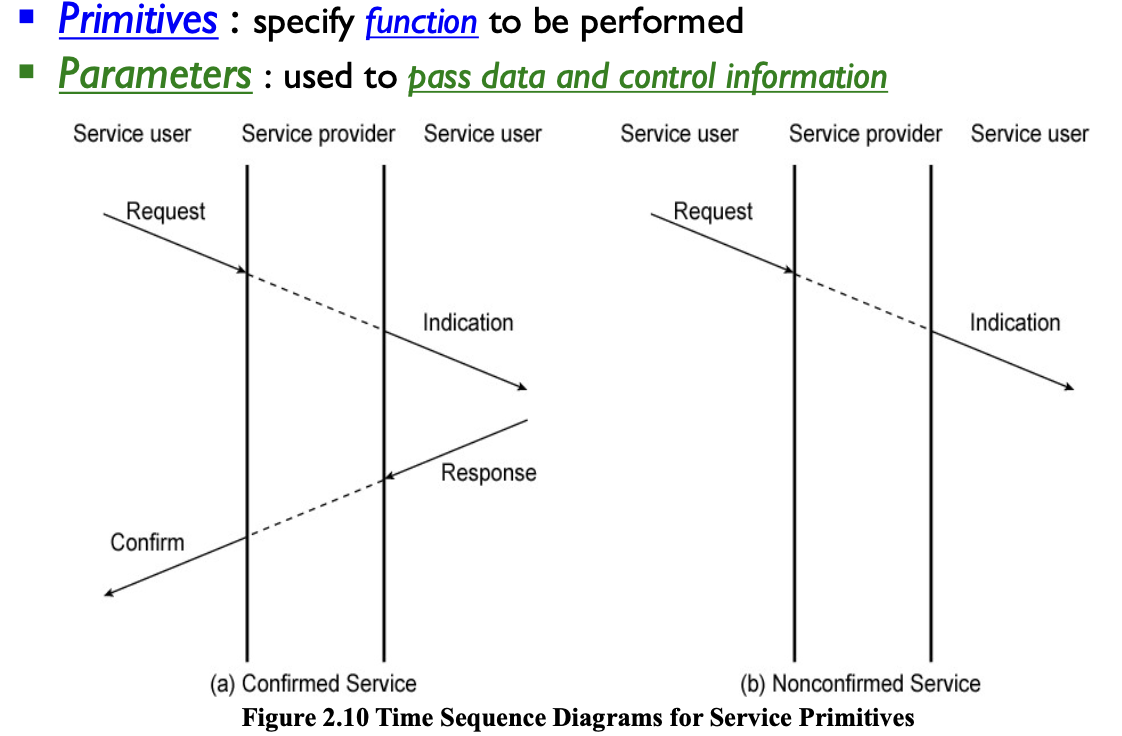
대표적으로, TCP는 Confirmed Service 라 볼 수 있고, UDP는 Nonconfirmed Service라고 볼 수 있다.
